

Peplies J, Glockner O, Amann R (2003) Optimization strategies for DNA microarray-based detection of bacteria with 16S rRNA-targeting oligonucleotide probes. Penna A, Galluzzi L (2013) The quantitative real-time PCR applications in the monitoring of marine harmful algal bloom (HAB) species. Mikulski CM, Park YT, Jones KL, Lee CK, Lim WA, Lee Y, Scholin CA, Doucette GJ (2008) Development and field application of rRNA-targeted probes for the detection of Cochlodinium polykrikoides Margalef in Korean coastal waters using whole cell and sandwich hybridization formats. Medlin LK (2013) Note: steps taken to optimise probe specificity and signal intensity prior to field validation of the MIDTAL (Microarray for the Detection of Toxic Algae). Kodani M, Mixson-Hayden T, Drobeniuc J, Kamili S (2014) Rapid and sensitive approach to simultaneous detection of genomes of hepatitis A, B, C, D and E viruses. Ki JS, Han MS (2006) A low-density oligonucleotide array study for parallel detection of harmful algal species using hybridisation of consensus PCR products of LSU rDNA D2 domain. Kegel JU, Amo YD, Medlin LK (2013) Introduction to project MIDTAL: its methods and samples from Arcachon Bay, France.
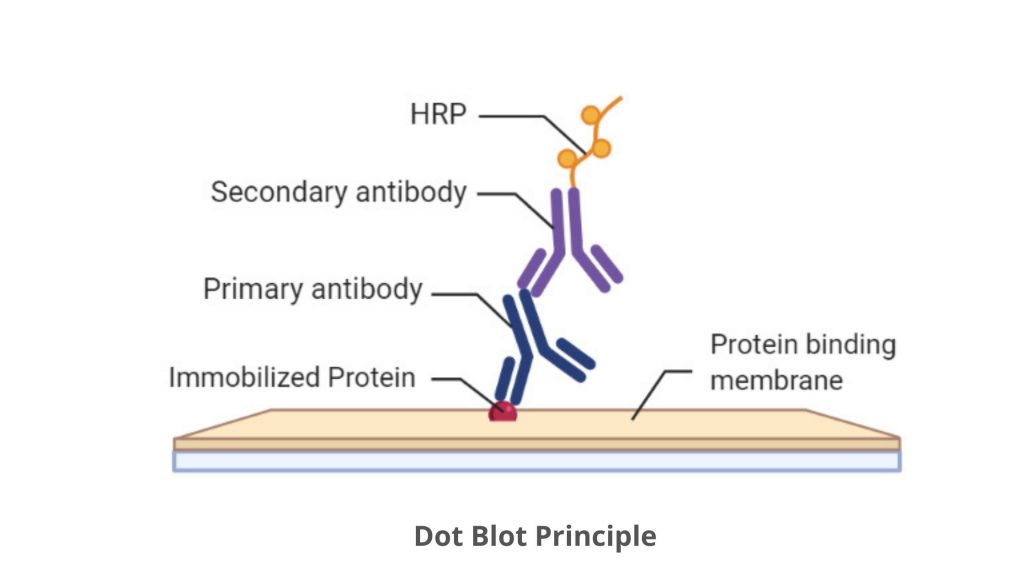
DNA DOT BLOT HYBRIDIZATION WINDOWS
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. Galluzzi L, Cegna A, Casabianca S, Penna A, Saunders N, Magnani M (2011) Development of an oligonucleotide microarray for the detection and monitoring of marine dinoflagellates. Mar Biol 160:953–960ĭiercks S, Metfies K, Medlin LK (2008) Development and adaptation of a multiprobe biosensor for the use in a semi-automated device for the detection of toxic algae. J Appl Phycol 25:1077–1089Ĭonnell LB (2001) Nuclear ITS region of the alga Heterosigma akashiwo (Chromophyta: Raphidophyceae) is identical in isolates from Atlantic and Pacific basins. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5742–5749Ĭhen GF, Liu Y, Zhang CY, Ma CS, Zhang BY, Wang GC (2013) Development of rRNA-targeted probes for detection of Prorocentrum micans (Dinophyceae) using whole cell in situ hybridization. These results indicate that RDBH can be a new technical platform for parallel discrimination of harmful algae and is promising for environmental monitoring of these microorganisms.Īhn S, Kulis DM, Erdner DL, Anderson DM, Walt DR (2006) Fiber-optic microarray for simultaneous detection of multiple harmful algal bloom species. The RDBH could recover all the target species from the simulated field samples and target species confirmed by the subsequent microscopy examination in the environmental samples. The detection performance of RDBH was relatively stable and not affected by non-target species and the fixation time of target species over at least 30 days. The developed RDBH demonstrated a detection limit up to 10 cells. The preparations of oligonucleotide array and hybridization conditions were optimized. The array produced a unique hybridization pattern for each target species differentiating them from each other. The digoxigenin (Dig)-labeled PCR products were denatured and then hybridized to the oligonucleotide array. Universal primers designed within the conserved regions were used to amplify the ITS sequences by using genomic DNA of target as templates. Each probe was oligo (dT)-tailed and spotted onto positively charged nylon membrane to make up a low-density oligonucleotide array. A set of specific probes for RDBH were developed by PCR, cloning, and sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS), alignment analysis, and probe design. Here, reverse dot blot hybridization (RDBH) was employed to simultaneously detect several harmful algae by using five representative bloom-forming microalgae along the Chinese coast. Warning and monitoring projects of harmful algal blooms require simple and rapid methods for simultaneous and accurate detection and identification of causative algae present in the environmental samples.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
